|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Attribute definitions |
  
|
|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Attribute definitions |
  
|
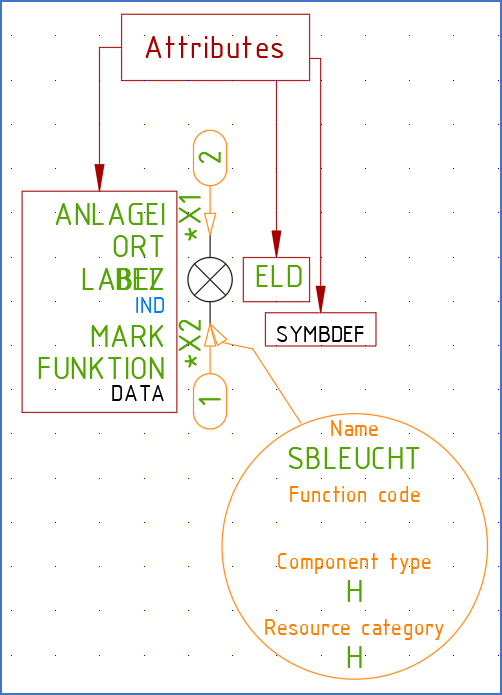
Figure 775: Attribute definitions in a cadett ELSA symbol being edited with the Symbol Generator
The names of the attributes in cadett ELSA are not configurable. The attribute for item designation is for instance always called BEZ, the remark is always called MARK and so on. Certainly, it is possible to define as many attributes as you need, but all standard attributes have their given names.
The Symbol Generator helps you with these names, so that you do not have to learn them by heart. Despite that, it might be a good idea to have at least a general idea of the most common ones, so that you for instance can recognise them in an “exploded” symbol.
The table below, lists a few examples.
Attribute name (TAG) |
Description |
|---|---|
IND |
Index, reference to the Catalogue
|
ANLAGEI |
= Function-oriented reference designation (plant)
|
ORT |
+ Location-oriented reference designation
|
CIRCUIT |
– Product-oriented reference designation or “circuit” in instrument documentation
|
BEZ |
Item designation or terminal group name
|
BEZ1 |
Terminal number, pin or socket number
|
LABEL
|
Symbolic (temporary) item designation |
FUNKTION |
Extra part of item designation for special needs, not to be mixed up with function-oriented reference designation (plant)
|
ELD |
Electrical data
|
MARK |
Remark
|
KNR1… |
Connection number, KNR1 used for the first one, KNR2 for the second one and so on
|
QVW |
Cross-reference from help symbol to main symbol
|
QVnnxxx |
Cross-reference from mirror symbol to help symbol nn = sequence number xxx = function code (like S=make, O=break, W=shift over)
|
SYMBDEF |
Backup of symbol database information, for instance connections, component type letter code and resource type, invisible (placed in the HIDE layer)
|
DATA |
Internal data, such as locking of item designations, invisible (placed in the HIDE layer)
|
SYMROTATION |
Rotation of the symbol object, invisible (placed in the HIDE layer)
|