|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> General composition |
  
|
|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> General composition |
  
|
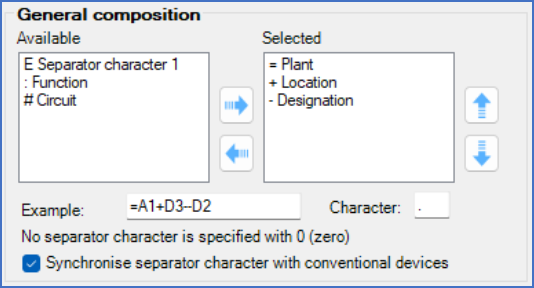
Figure 402: General composition
The General composition, which is the first level of the composition, is almost identical for Conventional devices, PLC, and Cables. The only difference is that absence for Conventional devices of the Synchronise separator character with conventional devices check-box, but the reason for that is of course obvious.
Below, the available parts for the General composition are presented. Other parts than the ones presented below cannot be used in this context.
Part |
Description |
|---|---|
Plant |
The Plant part is used for the "function aspect" according to IEC1346, and "function oriented high level designation" according to IEC750.
Plant/function is a way of dividing the design according to function, regardless of the location of individual components.
Plant/function is specified in the drawing frame (upper left corner according to IEC1082, in the title field according to older standards), in a boundary box, or in the plant attribute (ANLAGEI) of symbols.
|
Location |
The Location part is used for the "location aspect" according to IEC1346, and "physical location" according to IEC750.
Locations is a way of dividing the design according to location, regardless of the function of individual components.
Location is specified in the drawing frame (upper left corner according to IEC1082, in the title field according to older standards), in a boundary box, in the location attribute (ORT) of symbols.
|
Circuit |
The Circuit part has two typical uses:
•The "circuit" aspect in its instrument context. •The high level "product" aspect according to IEC1346.
Product is a way of dividing the design according to how a system is implemented and assembled. "The (product) structure shows the partitioning of a system into single objects with regard to the product aspect independently of where the product is located and which function it fulfils" (IEC81346-12)
Circuit/product may be specified in the drawing frame (upper left corner according to IEC1082, in the title field according to older standards), in a boundary box, or in the circuit attribute (CIRCUIT) of symbols.
The circuit/product aspect in cadett ELSA is equivalent with plant and location in that it may have levels in exactly the same way.
|
Designation |
The Designation part is used for the "component level" of the item designation, meaning the lowest level, and the part of the item designation that is typically written beside the symbol in the circuit diagram.
The content of the designation part is primarily fetched directly from the designation attribute (BEZ) of the symbols. The content of that attribute can be almost anything, with an arbitrary composition with an arbitrary meaning. For example, it may be composed of a component type letter code and a counting number, perhaps with a minus as separator character. In that way, item designations very similar to conventional separator character dependent ones, can be handled.
For automatically generated item designations, a separate configuration is used to specify the composition of the designation part. That configuration is located directly to the right of the General composition, in a section named Composition of the designation part.
The designation can be specified in a boundary box (generic symbol) or in the designation attribute (BEZ) of symbols.
|
Function |
The Function must not be confused with the function aspect (plant), which is something else. Function was originally used in item designation standards older than IEC1346 and IEC750. It was used for a "letter as a characteristic of an individual functional group".
However, the original use hardly matters any longer. What does matter, is that over the years, the function has been widely utilised for a number of other purposes, as for instance an additional character after the counting number, if such is desired, for example to allow multiple item designations with the same counting number.
Function may be specified in a boundary box or in the FUNKTION attribute of symbols.
This function is often used for special purposes, such as special requirements for internal company standards. Please note that function can not be specified in multiple levels, like plant, location and circuit.
|