|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Component type letter code |
  
|
|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Component type letter code |
  
|
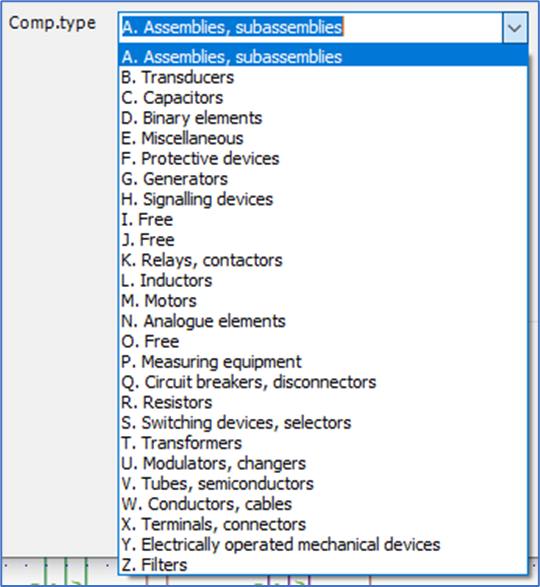
Figure 998: Selection of component type letter code
The component type letter code is defined for main symbols to be used by the automatic item designation generation feature. It simply specifies the default for the part of the product designation that precedes the counting number in the end of an item designation , like the "K" in -K1.
Typical component type letter codes are defined by IEC1346. Please note that the standard allows for the use of multiple characters. Please also note that cadett ELSA supports component type letter codes with up to five characters.
The older IEC750 standard also defined typical component type letter codes. The old standard was in fact more precise and in some ways more extensive, however also less general in character. Those differences have caused the influence of the old standard to still remain more than notable even today, 20 years after the official discontinuation.
Please refer to the table below, in which letter codes for which the standards mainly agree are marked with green. Letter codes where the standards mainly deviate are marked with red.
Letter code |
IEC1346 |
IEC750 |
|---|---|---|
A |
Shall not be used |
Assemblies, sub-assemblies |
B |
Sensing object |
Transducers, pilot switches |
C |
Storing object |
Capacitors |
D |
Reserved for future standardisation |
Binary elements |
E |
Emitting object |
Miscellaneous |
F |
Protecting object |
Protective devices, protective equipment |
G |
Generating object |
Generators, power supplies |
H |
Matter processing object |
Signalling devices |
I |
Shall not be used |
Not used |
J |
Reserved for future standardisation |
Not used |
K |
Information processing object |
Relays, contactors |
L |
Reserved for future standardisation |
Inductors |
M |
Driving object |
Motors |
N |
Covering object |
Analogue elements |
O |
Shall not be used |
Not used |
P |
Presenting object |
Measuring equipment |
Q |
Controlling object |
Circuit breakers, disconnectors |
R |
Restricting object |
Resistors |
S |
Human interaction object |
Switching devices, selectors |
T |
Transforming object |
Transformers |
U |
Holding object |
Modulators, changers |
V |
Reserved for future standardisation |
Tubes, semiconductors |
W |
Guiding object |
Conductors, cables |
X |
Interfacing object |
Terminals, connectors |
Y |
Reserved for future standardisation |
Electrically operated mechanical devices |
Z |
Reserved for future standardisation |
Filters |
Please also note that IEC1346 additionally provides definitions for both a second and a third level of the component type letter code, which can be used to divide components and functions in a more detailed way than the first letter provides (the so-called "entry class").
The table below shows an example of a few three level class codes. For the entire list, please refer to IEC 81346-2.
Level 1 |
Level 2 |
Level 3 |
Class name |
|---|---|---|---|
F |
Protecting object |
||
FA |
Over-voltage protecting object... |
||
FAA |
...by a spark gap |
||
FAB |
...by a varistor |
||
FAC |
...by a zener diode |
||
FAD |
...by surge absorption |
||
FB |
Earth fault current protecting object... |
||
FBA |
...that monitors an electric network and switches off in the event of earth fault currents |
||
FBB |
...that limits the value of an earth fault current |