|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Traditional IEC750-like implementation without levels |
  
|
|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Traditional IEC750-like implementation without levels |
  
|
In this IEC750-like IEC1346 implementation, three aspects are used:
•Function (=)
•Location (+)
•Product (-)
Function is sometimes referred to as “plant”, which is the name that was used in the old IEC750 standard, which was the predecessor of today’s IEC1346.
Function and location are specified without any levels.
Between function and location, and between location and product, a so-called transition occurs, when you go from one aspect to another.
A typical item designation could look like this:
=A1+C3-K1
In the old IEC750 standard, plant was called block 1 and location was called block 2.
The third part of the item designation marked with a minus character, was called block 3. The “product” aspect was not invented yet. Instead, this was called the “component level” of the item designation, normally referring to a single physical component, which isn’t that far away from what a product today can be.
In the dialogues of cadett ELSA, function is typically specified in the Plant attribute, while location is specified in the Location attribute. Product is typically specified in the Designation attribute.
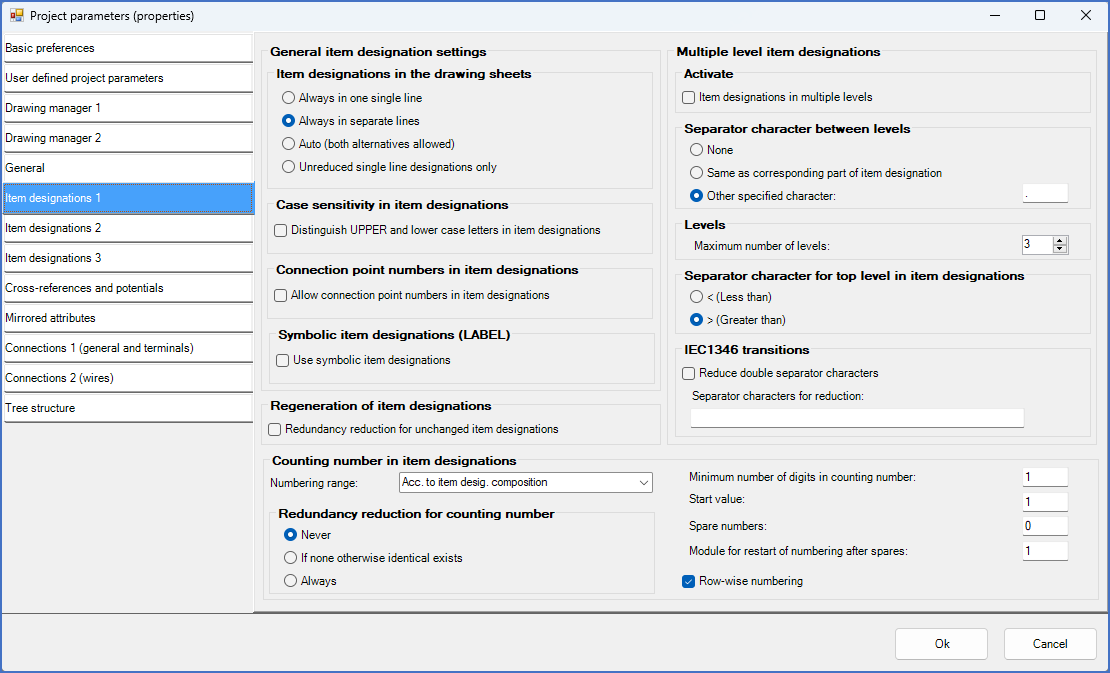
Figure 521: Please note that "Item designations in many levels" is inactive, and that "Separator character independent item designations" is inactive as well.
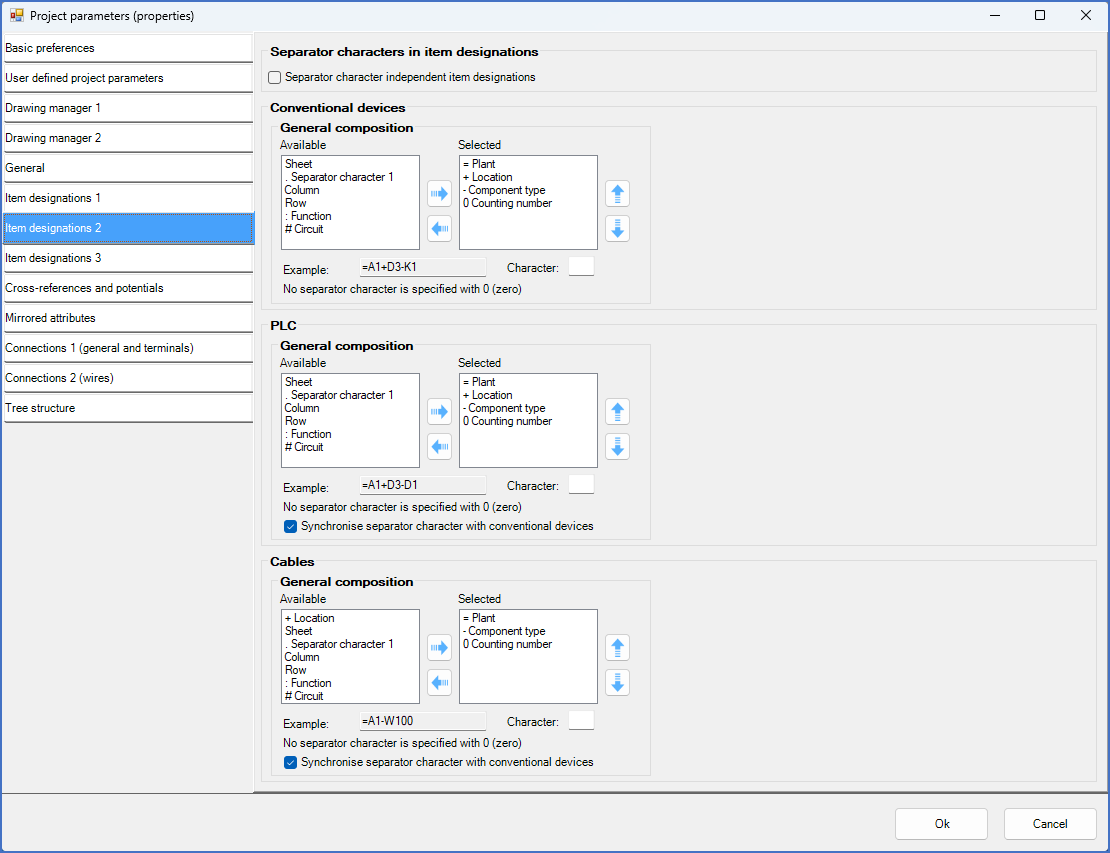
Figure 522: These settings are pretty conventional with three aspects in traditional sequence.
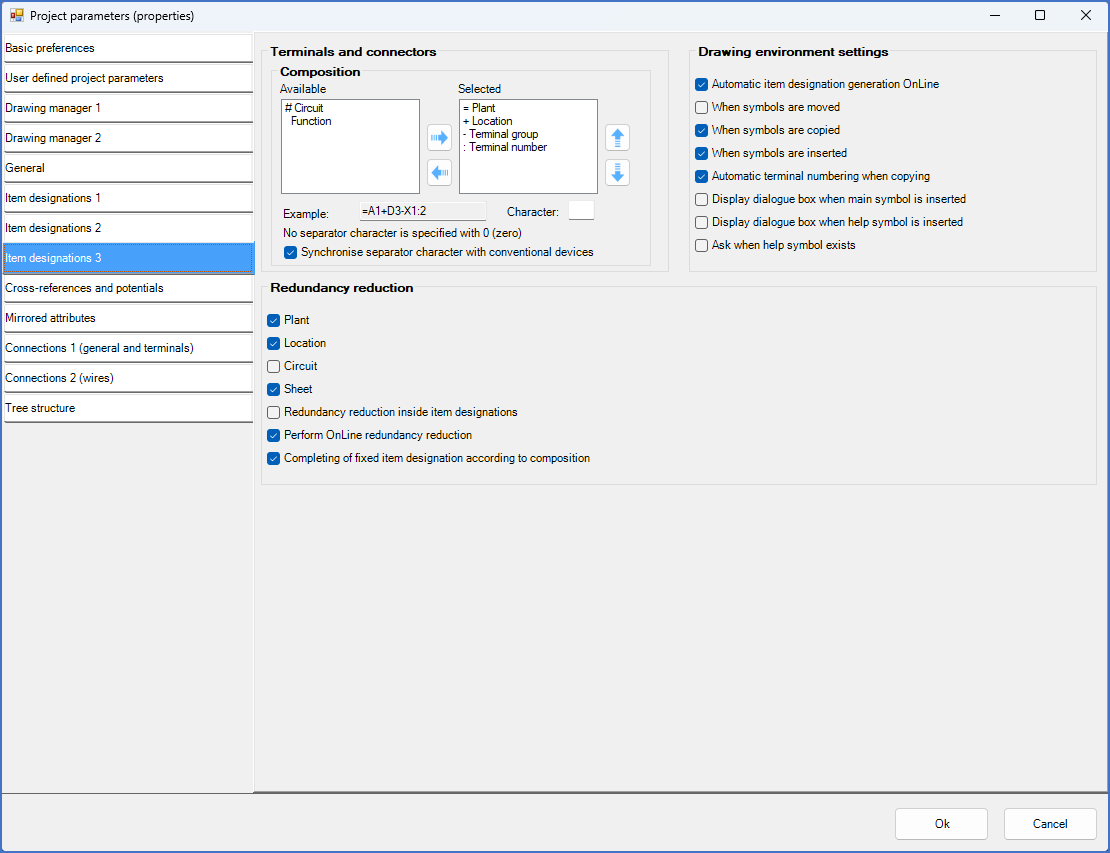
Figure 523: There are no surprises in the "Item designation 3" tab either.