|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Sheet numbering and cross-references |
  
|
|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Sheet numbering and cross-references |
  
|
Sheet numbering in the example will not only be made individually for each DCC code, but also individually for each function/plant.
Cross-references between drawing sheets therefore need to include both the DCC code and the function/plant designation. Otherwise, you would end up with ambiguous cross-references, for example referring to sheet 2, when there in fact are multiple sheets with sheet number 2.
Like in the full IEC1355 implementation, the document code is made up of up to six characters:
•Area, 1 character
•Main class, 1 character
•Sub-class, 1 character
•Counting number, 3 characters
The function/plant designation is made up of up to 12 characters, with 4 levels each consisting of up to 3 characters (4 x 3 = 12).
Example:
=G1=C1=K1=B1
The composition of the cross-references is as follows:
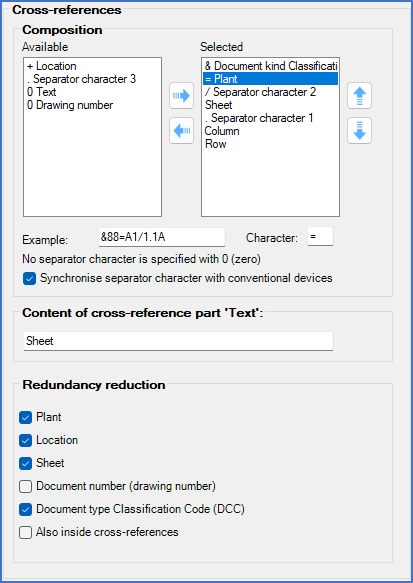
Figure 599: Cross-reference composition and redundancy reduction
Displayed in another way the composition is:
&Document_class_code =Plant / Sheet_number . Column Row
Example:
&EFS=G1=C1/5.3C
Redundancy reduction is active for Document kind Classification Code, Plant and Sheet number. This means that when referring within the same DCC code and function/plant from one circuit diagram to another, both the DCC code and the function/plant are omitted. The same is true for sheet number, so that references within the same sheet will not contain DCC code, function/plant and sheet number. Typical example:
/.3C
The drawing frame used in the example, is the standard ELSA390E.
The mask file, however, is customised in several ways. All details about the mask are described in the Title field links sub-topic.