|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Possible problems with cables |
  
|
|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Possible problems with cables |
  
|
A cable symbol is best placed in sub-nodes containing no more than two connections, meaning a simple point-to-point connection. In that case, you can be sure of getting an unambiguous interpretation. A cable core in a sub-node containing more than two connection points will be ambiguous, with several possible interpretations of between which two connection points the cable core is connected. In other words, the result may deviate from your expectation.
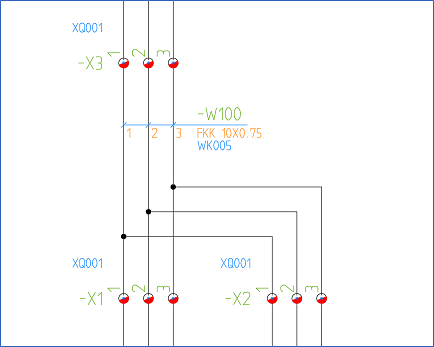
Figure 1681: What does this really mean? It is not unambiguous.
In such a situation, cadett ELSA will - in a way - make a guess. A sub-node that has three connection points contains two “wires” or so-called “vias”. The “vias” can be connected in three different ways:
If you have three connection points - 1, 2 and 3 - which are connected to each other, you may connect them in order 1-2-3, in order 1-3-2 or in order 2-1-3. In each of these cases, the cable core can be either one of the two “via's”. In other words, there are six possible interpretations of how the cable core and the remaining wire are connected (3 x 2 = 6).
If the number of connection points in a sub-node is greater than three, the number of interpretations is even greater. So, which interpretation will cadett ELSA select?
The connection points are sorted according to general connection handling rules. In a typical case, this means that cadett ELSA first sort them according to function (plant) and location, thereafter according to the cabinet layout if there is one, then after the component type letter code, then the counting number of the item designation, and finally after the connection number. The “via's” are connected in the same order. The first of these “via's”, counted in the sorted order, will constitute the cable core. You can in no way be sure that this is what you intended. To certify that you get the result that you want, you must take manual control.
There are two possible techniques to do so. One of them is called “wire number binding”, and the second one “forced connections”. Both methods are described in a sub-topic of the Dynamic OnLine I - Cable list topic named More complex nodes.
Please refer to the topic listed below.